Conic Independence
Conic Independence | Conic Independence |
|
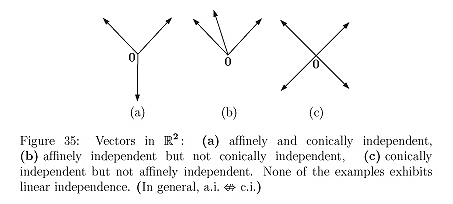
Conic independence is introduced as a natural extension to linear and affine independence; a new tool in convex analysis most useful for manipulation of cones. Perhaps the most useful application of conic independence is determination of the intersection of closed convex cones from their halfspace-descriptions, or representation of the sum of closed convex cones from their vertex-descriptions. A halfspace-description for the intersection of any number of closed convex cones K_i can be acquired by pruning normals; specifically, only the conically independent normals from the aggregate of all the halfspace-descriptions need be retained. Generators for the sum of any number of closed convex cones K_i can be determined by retaining only the conically independent generators from the aggregate of all the vertex-descriptions. Such conically independent sets are not necessarily unique or minimal. |